Blockchain and Bitcoin have been blooming since 2008. You may have heard of the bitcoin mining boom that was so popular a while back or the Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) which has been used for fraud.
As most people know, the decentralization of the blockchain and its immutable data structure can impose significant obstacles on hackers. The belief in “Passwordless” is what gave birth to AuthenTrend, it’s the same idea of giving people back their rights of data access. On the other hand, Blockchain encryption applications also seek to solve data storage issues, and while security and privacy concerns are addressed, at this stage transactions on blockchains still require people to log into their decentralized identities via PIN code or passwords, which is a problem that AuthenTrend has been eager to solve.
Blockchain = Bitcoin?
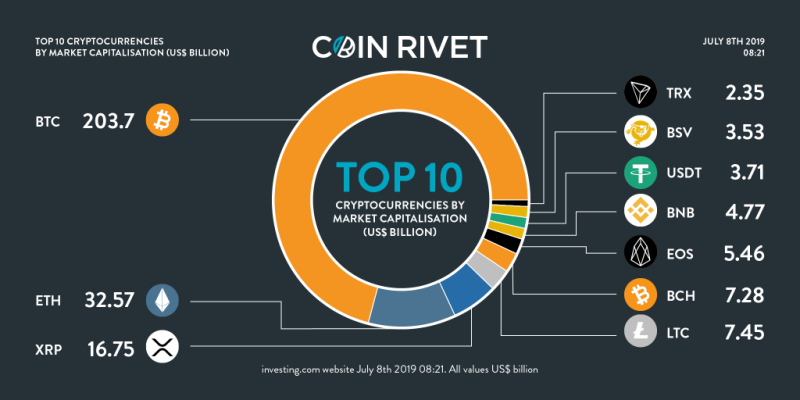
As you can see above, from the latest cryptocurrency market capitalization in July 2019, Bitcoin is still king among the coins, which is why most people have at least heard of it even if they don’t know much about blockchain.
BUT,Bitcoin ≠ Blockchain。
The Birth of Bitcoin — October 31, 2008 / 2:10 p.m. New York time
A man who called himself Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, which describes a decentralized framework for electronic transactions. He sent out an email to all his fellow cryptographers, hoping to create a decentralized, global digital transaction network. This is the Bitcoin system that is supposed to replace the Internet, and this paper has become the bible for all blockchain research worldwide.
No more intermediaries
In the long past, financial institutions acted as intermediaries for online transactions and at the same time, banks build a foundation of trust by collecting and examining personal information to take the trust risk between the two parties. While Bitcoin removes this middleman and replaces it with miners to help verify the transaction, allowing both parties to conduct P2P transactions directly.
Bitcoin is the first application of the blockchain
What is Blockchain:A public and distributed ledger
A Blockchain is a long chain that stores transaction history, with block after block containing tons of transactions that are secured and bound to each other using cryptographic principles.
- Block = A ”Transparent” safe with locked ledgers(Transactions) = Hash Value
- Chain = Crytographically (Note1:Hash ) connects each block.
In addition to the first block, each subsequent block will contain the hash value of the previous block (the Prev Hash in the diagram), plus its new transaction data and subsequent encryption steps.
How does Bitcoin work through the blockchain?
Since we compare “transparent” safe and chain with a blockchain, this means that blockchain information is public, shared, and difficult to be tampered with on the Internet.
Every transaction made on the Bitcoin blockchain is recorded anonymously in a blockchain ledger. At this point, the questions are usually asked:
Who keeps these blockchains;
and who is going to wind them up?
The key to blockchain technology, as mentioned in Satoshi Nakamoto’s paper, is for participants to jointly maintain this ledger in a shared, public, tamper-proof, and decentralized manner. Whenever a new bitcoin transaction is made, it is verified by other bitcoin users, and bitcoins are earned by verifying the transaction, which is commonly known as “mining”.
The question remains: who can be a miner? Who decides?
— This will be explained in the second half of the paragraph.
If you’re just wondering what a blockchain is, this diagram has condensed the terms and process framework I mentioned above; but if you want to pay for a Bitcoin, let’s keep going on a Bitcoin transaction journey that will take you through the blockchain application.
Learn applications of blockchain technology from a bitcoin trading journey
How Bitcoin Signatures Work: Understanding the Relationship Between Bitcoin Wallets, Public and Private Keys, and Addresses
- Transaction validation:
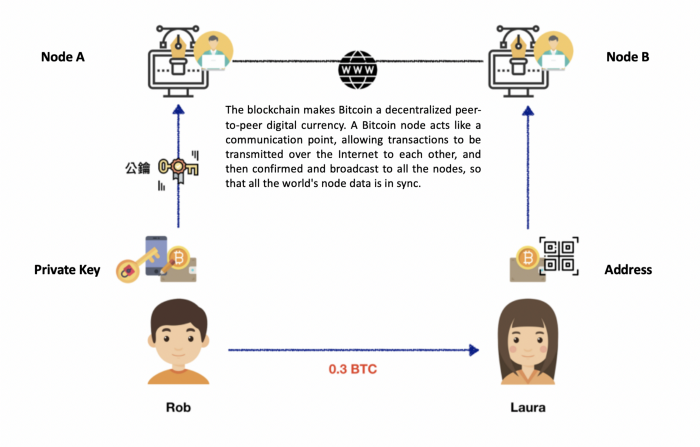
The story begins with Rob opening the “Bitcoin Wallet” on his phone, entering Laura’s address, amount and fee and quickly sending it out. It looks as simple as if we were transferring money from an Internet bank. In practice, how are bitcoin transactions verified through the blockchain without the intermediary role of a bank?
The full transaction validation on the blockchain is shown in the figure below:
- Bitcoin Addresses — Laura uses the public key to generate a bitcoin address via the Hash algorithm, which acts like a bank account and can generate many addresses for anyone who transfers bitcoins to you. Also, the bitcoin address is anonymous and does not contain any personal information.
- Public/Private Key — Rob takes his private key, digitally signs the transaction “0.3 Bitcoin to Laura” (just like the way people sign documents in real life), and then broadcasts the signed transaction to Node A. Node A takes Rob’s public key and digitally signs the transaction. Node A will validate the transaction with Rob’s public key, and if the validation is correct, the transaction must have been initiated by Rob, because only Rob has the private key. If someone decrypts the transaction and tampered with the content in the middle of the transaction, since that person does not have Rob’s private key to re-sign, the tampered content will not pass public key verification. Thus, the role of the private-public key system is to ensure the authenticity of the transaction.
- Bitcoin wallets are used to store private keys, such as our bank’s seals and passbooks. Most people use an online hot wallet to manage and store private keys, bitcoin addresses and blockchain data in an app. Or an offline cold wallet for added security.
2. Miners grab a piece of the pie:Proof of Work
The consensus mechanism for determining who the miners are, as mentioned earlier, is called Proof of Work (PoW).
Work means mining, and mining is when miners contribute their computing power to solving a difficult mathematical function, which requires constant attempts at calculation to calculate the answer, and the first to find the correct answer is the miner who will be able to create the block and is rewarded for doing so. This means that the more computing power there is, the higher the chance of creating a new block, and the reward in the bitcoin blockchain is bitcoins.
In addition to the PoW used in Bitcoin, there are other consensus mechanisms used in other blockchains, such as the PoW, the PoS, and the DPoS. Consensus mechanisms are an essential core mechanism in the development of a blockchain and are bound to evolve and evolve themselves.
3. How does a shared ledger look like?
Once Laura receives her bitcoins, the transaction information is publicly available on the blockchain. There are many blockchain online browsers such as Blockchain.com、BlockExplorer, etc. that allow us to see the updated data on the bitcoin blockchain, as shown in the image below, where we can see the number of bitcoin transactions, the time of the transaction, the addresses of the wallets of both parties, and more.
4. Hot wallet Vs. Cold wallet: How should you store your Bitcoin and keep it safe?
Hot wallet
A hot wallet is more common and It is an online client connected to the internet. There are several popular hot wallets for the Ethereum network which work on your web browser, such as MyEtherWallet. If you download a wallet to your desktop or your phone, that is also a hot wallet because it is connected to the internet.
Most exchanges usually utilize hot wallets. One of the pros is that this allows for fast access to user funds. However, it also means if you are storing your funds on an exchange with these practices, your funds are more at risk of hacking.
Cold wallet
A cold wallet is unloaded so that hackers have a harder time accessing your stored coins for improved security. For any cryptocurrencies that you don’t need instant access to, it’s best to store them offline in a cold wallet. The private key is always offline that can maintain high levels of security is key in crypto.
There are different choices of cold wallets, such as a hardware wallet or a paper wallet. A hardware wallet is an external device like a Ledger Nano S or Trezor that stores your private keys. In general, these popular hardware wallet access is locked behind a password or pin that you have to insert PIN code every time.
But most of the cold wallets on the market still require PIN code protection. And there are usually only support USB or BLE, and users always need a PC or phone to connect to your wallet. However, we create a card type wallet with standalone mode for quick checking and transactions, that is
secure, private and easy to verify to use. In addition to the common mechanisms available on the market, our security is a combination of
biometrics so that users’ identities both in the virtual world and the real world are protected.
AuthenTrend has a close strategic tie with Egis Technology, which enables us to provide this small, reliable and with the high-performance fingerprint card. Our patented standalone mode makes users verify their fingerprint quickly and check cryptocurrency amounts or do transactions through builtin low power consuming E-Ink display. We will provide the most secure, reliable and at the same time easy-to-use hardware wallet.
Learn More about AT.Wallet
Get your AT.Wallet here: AT.Wallet just passed IP68 waterproof test and won a prize at CES 2020 Innovation Award Honoree.
If you are interested in any of our AT.Wallet’ technical details, please feel free to contact us.
[contact_box title=”AuthenTrend” email=”contact@authentrend.com” www=”www.authentrend.com” image=”https://authentrend.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/AuthenTrend-Website-C-1.png” animate=””]